For more details about an impact, contact information for NMSU ACES faculty and staff is available at the online directory.
For general questions regarding impacts in this database, please contact Claire Montoya at ccortner@nmsu.edu.
Impacts
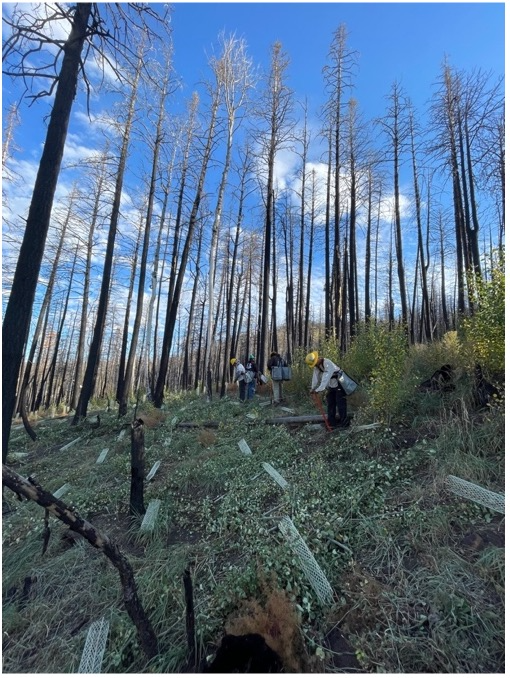

The JTH Forestry Research Center, in collaboration with the University of New Mexico, is researching nucleation planting to improve forest resilience in the southwestern U.S. This innovative approach mimics natural regeneration by planting small tree clusters, aiming to reduce fire risk and enhance drought resistance. Key research focuses include using seedling survival models to guide planting locations, testing a range of planting densities, and evaluating the impact of competing vegetation. In 2024, over 5,000 seedlings were planted in the Hermit’s Peak/Calf Canyon wildfire-impacted area, with active contributions from tribal communities. This long-term study seeks to optimize reforestation practices, leveraging model-based site selection and fostering collaboration to promote sustainable and climate-resilient ecosystems.
More...
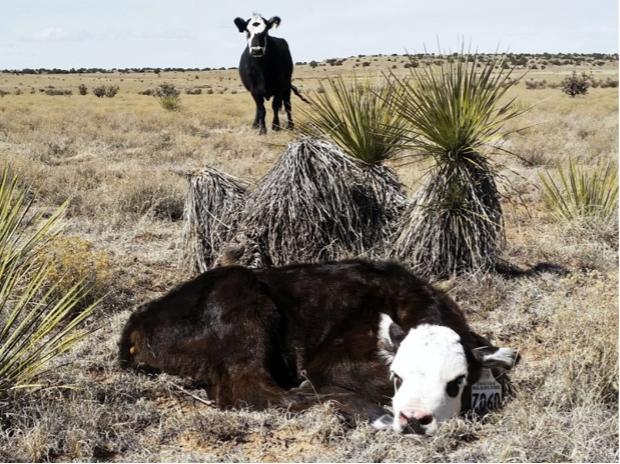

Provision of supplemental arginine during early gestation can improve an animal’s ability to metabolize energy, which increases growth, health, and reproductive success. In combination, these benefits ultimately improve the longevity of beef females and the sustainability of the livestock producer.
More...
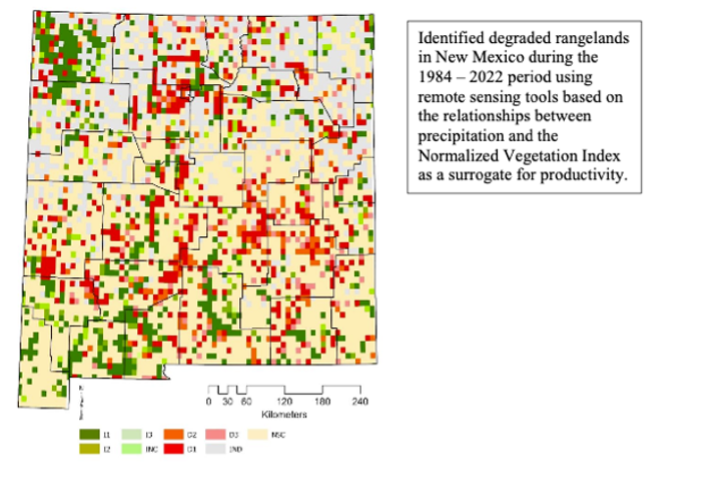
Assessment of Arid Land Sustainability Through Drought and Wildfire Management Drought and wildfire are major natural hazards that affect New Mexico’s ecosystems sustainability due to climate change. Two NOAA-funded projects aim to identify vulnerable regions and communities across New Mexico, document how affected communities use science-based tools to adapt to these natural hazard and identify current gaps to enhance their use to support the sustainability of arid land ecosystems.
More...

Biological Control has the potential to control many insect pests but is frequently undervalued. Control of insect eggs alone is often over 80% when populations of predators are not disrupted by frequent insecticide applications. The ASC farm has maintained good control of alfalfa weevil with biological control for 20 years. Replicating this type of control in just alfalfa and pecan will save growers over $6.5 million per year in reduced losses and control costs.
More...

Healthy soils provide the foundation for sustainable agriculture. Research at multiple locations in eastern New Mexico and Colorado to study soil health responses and associated ecosystem functions revealed multiple benefits of cover cropping and compost addition in dryland and limited-irrigation cropping systems.
More...

Pecans are a large contributor to New Mexico’s agricultural economy with production exceeding $130 million annually.
More...

Effective water management is a critical challenge faced by turfgrass managers in arid regions worldwide and periodically in temperate zones. Governments have responded to reduced water supplies by implementing policies that restrict potable water use for non-essential purposes. Despite ongoing efforts to reduce water consumption and showcase water conservation in turfgrass management, additional water restrictions will persist, limiting turfgrass water use.
More...
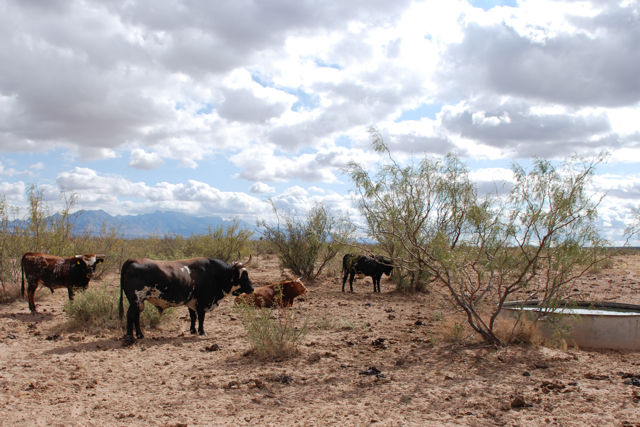

An NMSU researcher led an effort to understand how beef genetics impact the profitability of beef production in arid environments. Significant challenges for raising beef cattle exist in the arid and semi-arid regions of the United States. Limited forage availability and small profit margins are among the greatest concerns in Western U.S. ranching operations. One potential option for ranchers in these regions is using alternative cattle genetics, such as Raramuri Criollo (RC), a Mexican heritage biotype of cattle brought to the Americas by Spanish Conquistadors.
More...

Vineyards and wineries are adapting- grape growing, production, and marketing to meet the rising demand for sustainable products. Wine consumers show a growing inclination to consider how products impact the natural environment, while generational differences impact sustainable wine choices.
More...
(No image)
According to the USDA, food insecurity is defined as a lack of consistent access to enough food for an active, healthy life. In New Mexico, one-third of the state’s population experienced food insecurity in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. This number is three times higher than the national average of 10.5%. In the state, the lack of access to food is partially due to the high incidence of food deserts, which are areas where a substantial number of residents do not have easy access to a supermarket or large grocery store, and approximately 30% of New Mexico counties are considered food deserts.
More...